Calf cramps can be caused by dehydration, muscle fatigue, or mineral deficiencies, and understanding the triggers can help alleviate them.
Cramps in the calves can be an uncomfortable and often painful experience. They can strike at any time, whether you’re exercising, sleeping, or even sitting still. Understanding why these cramps happen can provide insight into how to prevent them and improve overall muscle health.
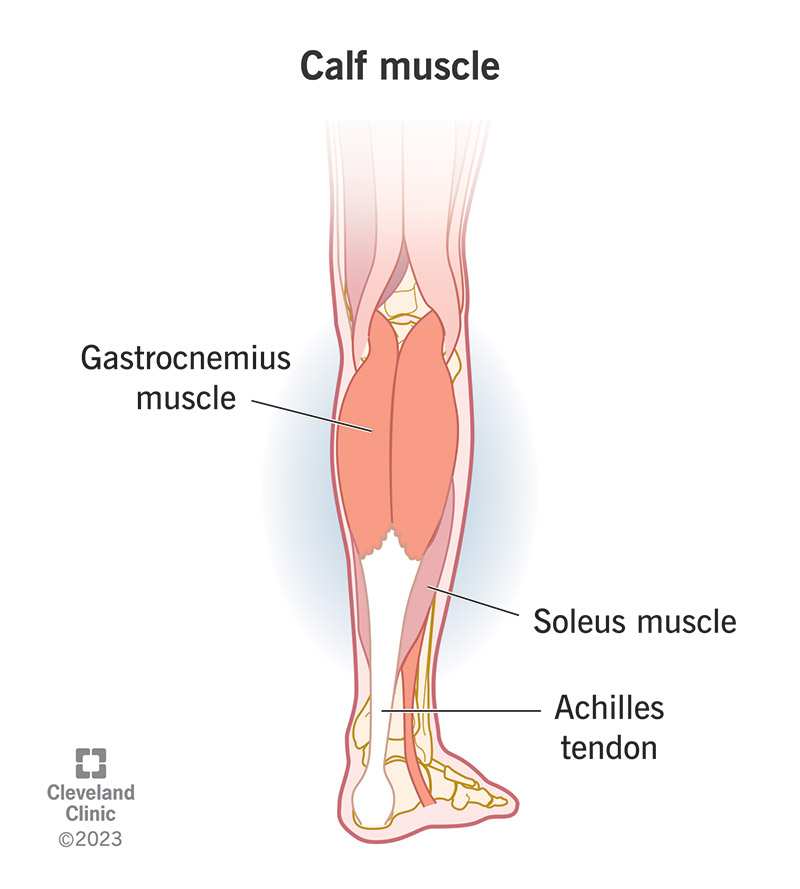
The Anatomy of Calf Muscles
The calf consists primarily of two muscles: the gastrocnemius and the soleus. The gastrocnemius is the larger muscle that gives the calf its shape and is responsible for movements such as running and jumping. The soleus lies beneath it and plays a crucial role in walking and standing. Both muscles work together to facilitate movement and maintain balance.
When these muscles contract involuntarily, they cause a cramp. This involuntary contraction can be triggered by various factors, including dehydration or overexertion during physical activity. Understanding these muscles’ functionality helps clarify why cramps occur in the first place.
Common Causes of Calf Cramps
Calf cramps are often a result of several underlying issues. Identifying these causes is crucial for effective prevention.
Dehydration
One of the primary culprits behind calf cramps is dehydration. When the body loses more fluids than it takes in, it can lead to an imbalance in electrolytes like sodium, potassium, calcium, and magnesium. These electrolytes are essential for muscle function. A lack of adequate hydration can cause muscles to become irritable and prone to cramping.
Muscle Fatigue
Overexertion during physical activity is another common cause of calf cramps. Intense workouts that push the muscles beyond their limits can lead to fatigue, making them more susceptible to cramping. This is particularly true for activities that involve repetitive motions or prolonged periods of standing or running.
Mineral Deficiencies
Deficiencies in essential minerals such as potassium, calcium, or magnesium can also trigger cramps. These minerals play vital roles in muscle contraction and relaxation. A lack of any one of them may disrupt normal muscle function and lead to painful contractions.
Poor Circulation
Circulation issues can contribute to calf cramps as well. Reduced blood flow to the legs due to conditions like peripheral artery disease (PAD) may result in cramping during physical activity. When blood flow is restricted, muscles may not receive enough oxygen or nutrients needed for optimal performance.
Symptoms Associated with Calf Cramps
Recognizing the symptoms associated with calf cramps can help differentiate between different types of pain one might experience in this area.
Pain Intensity
Calf cramps are often described as sudden, sharp pain that occurs unexpectedly. The intensity can vary from mild discomfort to severe pain that makes it difficult to walk or move the affected leg.
Duration
Typically, a calf cramp lasts anywhere from a few seconds to several minutes. While most cramps resolve quickly on their own, they may recur multiple times throughout a single day or over several days.
Location
The location of the pain is generally localized within the calf muscle itself but may radiate into adjacent areas such as the foot or ankle during intense episodes.
Preventive Measures for Calf Cramps
Taking proactive steps can significantly reduce the chances of experiencing calf cramps.
Stay Hydrated
Maintaining proper hydration is essential for preventing muscle cramps. Drinking plenty of water throughout the day helps keep electrolyte levels balanced and supports overall muscle function.
Stretching Exercises
Incorporating stretching exercises into a daily routine can enhance flexibility and reduce tension in calf muscles. Simple stretches such as standing calf raises or seated toe stretches help keep muscles limber and less prone to cramping.
Balanced Diet
Eating a balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats ensures adequate intake of essential minerals like potassium, magnesium, and calcium. Foods such as bananas, spinach, yogurt, nuts, and seeds are excellent choices for supporting muscle health.
Treatment Options for Calf Cramps
When cramps do occur despite preventive measures, understanding how to treat them effectively makes all the difference.
Immediate Relief Techniques
If a calf cramp strikes unexpectedly, there are several techniques one can try for immediate relief:
- Gentle Stretching: Straightening out the leg while flexing the foot upward towards your shin helps stretch out tight calf muscles.
- Massage: Gently massaging the affected area promotes blood flow and eases tension.
- Heat Therapy: Applying heat through a warm towel or heating pad relaxes tight muscles.
| Treatment Method | Description |
|---|---|
| Gentle Stretching | Flexing foot upwards while straightening leg. |
| Massage | Gently working on tight areas to promote blood flow. |
| Heat Therapy | Applying warmth helps relax tightness. |
| Cryotherapy | Icing reduces inflammation post-exercise. |
| Epsom Salt Soak | A soak with Epsom salt may relieve soreness. |
The Role of Exercise in Calf Health
Regular exercise contributes significantly to maintaining healthy calves but must be approached mindfully.
Adequate Warm-Up/H4>
Warming up before engaging in any physical activity prepares muscles for exertion by increasing blood flow and flexibility. A good warm-up routine should include dynamic stretches targeting not only calves but also other major muscle groups involved in your activity.
Cross-Training/H4>
Incorporating various forms of exercise into one’s routine helps prevent overuse injuries associated with repetitive activities like running or cycling alone. Cross-training allows different muscle groups to engage while providing rest periods for others—ultimately reducing fatigue-related cramps.
The Importance of Rest/H4>
Rest plays an integral role in recovery after intense workouts or long periods on your feet; allowing calves time to recuperate enhances overall performance levels while minimizing cramping incidents down the line.
Key Takeaways: Cramps in My Calves
➤ Hydration is Key: Staying hydrated helps maintain electrolyte balance.
➤ Muscle Fatigue Matters: Overexertion increases susceptibility to cramps.
➤ Mineral Intake: Consuming potassium, calcium, and magnesium is vital.
➤ Stretch Regularly: Daily stretching reduces muscle tension and cramping.
➤ Recognize Symptoms: Sudden pain and duration can help identify cramps.
➤ Recognize Symptoms: Sudden pain and duration can help identify cramps.
Frequently Asked Questions: Why Do I Have Cramps in My Calves?
What are the main causes of cramps in my calves?
Cramps in the calves can stem from several factors. Dehydration is a leading cause, as it disrupts electrolyte balance crucial for muscle function. Muscle fatigue from overexertion during activities can also trigger cramps, making muscles more susceptible to involuntary contractions. Additionally, mineral deficiencies, particularly in potassium, calcium, or magnesium, can hinder normal muscle performance and lead to cramping. Understanding these causes is essential for prevention.
How can hydration prevent calf cramps?
Staying hydrated is vital for muscle health and preventing cramps. When the body loses fluids, it affects electrolyte levels, which are necessary for proper muscle contraction and relaxation. Drinking sufficient water helps maintain this balance. Electrolytes, such as sodium and potassium, play a key role in muscle function; without adequate hydration, muscles may become irritable and prone to cramping. Regular hydration before, during, and after physical activities is crucial for minimizing cramps.
What role do stretching exercises play in calf health?
Stretching exercises are essential for maintaining calf muscle flexibility and reducing tension. Incorporating stretches into your routine can help alleviate tightness that leads to cramps. Simple stretches like standing calf raises or seated toe stretches enhance blood flow and keep muscles limber. Regular stretching encourages better range of motion and prepares muscles for exertion, ultimately decreasing the likelihood of experiencing painful cramps during activities.
Are there specific dietary recommendations to avoid calf cramps?
A balanced diet rich in essential minerals is crucial for preventing calf cramps. Consuming foods high in potassium (like bananas), magnesium (found in nuts), and calcium (present in dairy products) supports muscle function. A diet comprising fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats ensures adequate nutrient intake necessary for optimal muscle health. Proper nutrition not only aids in preventing cramps but also enhances overall physical performance.
What immediate relief techniques can I use during a calf cramp?
If you experience a calf cramp, several immediate relief techniques can help ease discomfort. Gentle stretching, such as flexing the foot upwards while straightening the leg, effectively alleviates tension in tight muscles. Massage of the affected area promotes blood flow and reduces tightness. Applying heat therapy, such as using a warm towel or heating pad on the cramp site, can also relax the muscles and provide comfort during an episode.
Conclusion – Why Do I Have Cramps in My Calves?
Understanding why calves cramp involves recognizing various causative factors like dehydration, fatigue from exercise routines gone awry—alongside nutritional deficiencies—and circulation issues—all contributing towards those sudden painful episodes we dread experiencing! By implementing preventive measures such as staying hydrated through proper nutrition alongside regular stretching routines while also ensuring adequate warm-ups before workouts; one might find themselves better equipped against future bouts!