Typically, a healthy adult urinates between 4 to 8 times a day, depending on various factors like fluid intake and overall health.
The frequency of urination is a topic that often goes unspoken. It’s something that many people experience daily, yet few discuss openly. Understanding how many times a person should pee in a day can provide insight into one’s health and hydration levels. The question of “How Many Pees A Day Is Normal?” can be influenced by numerous factors, including age, diet, fluid intake, and even environmental conditions.
The average adult typically urinates about 6 to 8 times a day. However, this number can vary widely among individuals. Factors such as hydration levels, physical activity, and even the temperature can influence urinary frequency. For instance, someone who drinks a lot of fluids or consumes diuretic substances like caffeine may find themselves visiting the restroom more often.
Understanding Urination Frequency
Urination is the body’s way of removing waste and regulating fluid balance. The kidneys filter blood to create urine, which is then stored in the bladder until it is expelled from the body. This process is essential for maintaining homeostasis and ensuring that the body functions properly.
Several factors contribute to how often someone might need to urinate:
1. Fluid Intake: The amount of fluids consumed directly affects how often one needs to pee. More fluids mean more frequent trips to the restroom.
2. Diet: Certain foods can have diuretic effects. For example, beverages like coffee or alcohol can increase urination frequency.
3. Physical Activity: Exercise can lead to increased sweating, which may decrease urine output temporarily.
4. Medications: Some medications act as diuretics and can significantly increase urination frequency.
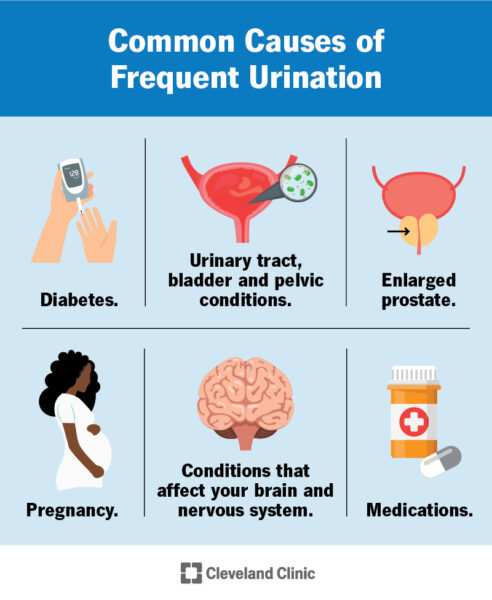
5. Health Conditions: Conditions such as diabetes or urinary tract infections can also affect how often one needs to urinate.
Understanding these factors can help individuals gauge whether their urination habits fall within a normal range.
Normal Urination Patterns
To better visualize typical urination patterns, consider the following table that outlines average daily urination based on various factors:
| Factor | Normal Urination Frequency (Times/Day) |
|---|---|
| Average Adult (Hydrated) | 6-8 |
| Increased Fluid Intake | 8-12+ |
| Caffeine Consumption | 7-10 |
| Alcohol Consumption | 7-12+ |
| High Physical Activity | 4-6 (may decrease due to sweating) |
| Elderly Individuals | 4-6 (may decrease due to decreased bladder capacity) |
| Pregnant Women | 6-10 (increased pressure on bladder) |
| Individuals with Diabetes | 8-15+ (due to increased fluid intake) |
| Individuals with UTIs | Varies (may experience urgency and frequency) |
This table illustrates just how varied normal urination patterns can be based on individual circumstances.
The Role of Hydration in Urinary Frequency
Hydration plays an essential role in determining how many times someone will need to urinate throughout the day. Water is crucial for kidney function; without adequate hydration, urine becomes concentrated and darker in color. This concentration can signal dehydration.
It’s important to drink enough fluids daily for optimal health. The commonly recommended amount is about 8 cups (64 ounces) per day for an average adult, but this varies based on individual needs and activity levels.
Some signs of adequate hydration include:
- Light yellow urine
- Regular bathroom visits
- No feelings of extreme thirst
Conversely, signs of dehydration might include dark yellow urine, infrequent bathroom visits (fewer than 4 times a day), dry mouth, and fatigue.
Maintaining proper hydration not only supports urinary health but also enhances overall bodily functions.
The Impact of Diet on Urinary Health
Diet significantly influences urinary frequency and health. Certain foods and beverages have diuretic properties that encourage more frequent urination:
1. Caffeine: Found in coffee, tea, and some sodas, caffeine stimulates the bladder muscle.
2. Alcohol: Acts as a diuretic by inhibiting vasopressin secretion—this hormone helps regulate water retention.
3. Spicy Foods: Can irritate the bladder lining in some individuals.
4. High-Salt Foods: May cause increased thirst leading to higher fluid intake and more frequent urination.
5. Fruits: Water-rich fruits like watermelon or cucumber contribute to overall fluid intake.
Conversely, some foods may help reduce urinary frequency by promoting better bladder health:
- Whole Grains: Help maintain healthy digestion.
- Lean Proteins: Support overall bodily functions without irritating the bladder.
- Low-Acid Vegetables: Such as carrots or spinach may soothe an irritated bladder.
Balancing these dietary elements can help manage urinary habits effectively.
The Influence of Age on Urinary Patterns
Age plays a significant role in urinary frequency and patterns as well. In children and young adults, bladder capacity is typically higher than in older adults who may experience reduced capacity due to age-related changes in muscle tone or nerve function.
Elderly individuals often report needing to urinate more frequently due to several factors:
1. Decreased Bladder Capacity: As people age, their bladders may hold less urine.
2. Medications: Many older adults take medications that affect bladder control.
3. Health Conditions: Chronic conditions such as prostate enlargement in men or pelvic floor issues in women can lead to increased urgency and frequency.
Similarly, pregnant women experience changes in urinary patterns due to hormonal fluctuations and increased pressure on the bladder from the growing uterus.
Understanding these age-related changes helps contextualize variations in urinary habits throughout life.
The Connection Between Health Conditions and Urinary Frequency
Certain medical conditions have profound effects on how often one urinates each day:
1. Diabetes Mellitus: High blood sugar levels lead to increased thirst and consequently higher fluid intake; this results in more frequent urination.
2. Urinary Tract Infections (UTIs): These infections cause irritation of the bladder lining leading to increased urgency and frequency with little urine produced each time.
3. Prostate Issues: In men, conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) can cause frequent urges due to obstruction of urine flow.
4. Bladder Disorders: Overactive bladder syndrome leads individuals to feel sudden urges frequently throughout the day regardless of actual volume produced.
5. Kidney Disease: Chronic kidney disease affects urine production leading either to decreased output or increased frequency depending on stage severity.
Recognizing these conditions allows for timely medical intervention when necessary.
The Psychological Aspect of Urinary Frequency
Psychological factors also play a role in how frequently someone feels the urge to pee:
1. Anxiety Disorders: Increased anxiety may heighten awareness of bodily sensations including urges for urination.
2. Stress Levels: Stress impacts overall bodily functions including those related directly or indirectly with urinary control.
3. Habitual Patterns: Some individuals develop habitual behaviors around bathroom use regardless if they genuinely need it—this could stem from past experiences or social conditioning.
Being aware of these psychological influences helps individuals better understand their own patterns regarding bathroom use without attributing them solely to physical causes.
The Importance of Monitoring Urinary Health
Keeping track of urinary habits is crucial for maintaining overall health—especially if any unusual changes occur such as:
- Significant increases or decreases in frequency
- Changes in color or odor
- Pain during urination
These symptoms could indicate underlying issues requiring medical attention such as infections or other health concerns.
For those who notice consistent changes outside what they consider normal—like asking oneself “How Many Pees A Day Is Normal?”—consulting with healthcare professionals could provide clarity about potential causes behind those shifts while ensuring optimal well-being remains prioritized moving forward.
Key Takeaways: How Many Pees A Day Is Normal?
➤ Normal Frequency: Healthy adults typically urinate 4 to 8 times daily.
➤ Fluid Intake Matters: Increased hydration leads to more frequent bathroom visits.
➤ Diet Influences Urination: Caffeine and alcohol can increase urination frequency.
➤ Age-Related Changes: Elderly individuals may experience reduced bladder capacity.
➤ Health Conditions Impact: Conditions like diabetes can lead to increased urination.
➤ Health Conditions Impact: Conditions like diabetes can lead to increased urination.
Frequently Asked Questions: How Many Pees A Day Is Normal?
What factors influence how many pees a day is normal?
The frequency of urination is influenced by various factors, including fluid intake, diet, and physical activity. For example, individuals who consume large amounts of fluids will likely urinate more frequently. Additionally, certain foods and beverages, particularly those with diuretic properties like caffeine and alcohol, can increase urination frequency.
Age also plays a role; elderly individuals may experience reduced bladder capacity, leading to more frequent trips to the restroom. Understanding these factors is essential for assessing what constitutes a normal pattern for each person.
How does hydration affect how many pees a day is normal?
Hydration significantly impacts urinary frequency. Adequate fluid intake helps maintain optimal kidney function and ensures urine is produced at healthy levels. When well-hydrated, individuals typically find their urine is light yellow in color, indicating proper hydration.
If someone becomes dehydrated, urine may become darker and less frequent. Maintaining proper hydration not only supports urinary health but also affects overall bodily functions. Thus, drinking enough water daily is vital for maintaining a normal urination pattern.
Can diet affect how many pees a day is normal?
Yes, diet plays a crucial role in determining urinary frequency. Foods and beverages can have diuretic effects that lead to increased urination. For instance, caffeine, found in coffee and tea, stimulates the bladder muscle.
Similarly, alcohol inhibits vasopressin secretion, which regulates water retention in the body. Conversely, foods like whole grains and lean proteins can promote better bladder health and potentially reduce the frequency of urination when consumed regularly.
How does age impact how many pees a day is normal?
Age significantly influences urinary patterns. In older adults, decreased bladder capacity often leads to more frequent urges to urinate. This change occurs due to age-related changes in muscle tone and nerve function.
Pregnant women also experience shifts in urinary habits due to hormonal changes and increased pressure on the bladder from the growing uterus. Understanding these age-related changes helps contextualize variations in urinary habits throughout life.
What are some signs that indicate abnormal urination frequency?
Monitoring urination habits is essential for overall health. Signs indicating an abnormal frequency include significant increases or decreases in the number of times one needs to urinate daily. Changes in urine color or odor may also signal underlying issues.
Pain during urination or experiencing urgency without producing much urine could indicate infections or other health concerns requiring medical attention. If any unusual patterns arise, consulting with healthcare professionals can provide clarity on potential causes.
Conclusion – How Many Pees A Day Is Normal?
Most adults find themselves peeing between 4–8 times daily; however this number varies widely based upon individual circumstances surrounding hydration levels alongside dietary choices among others! Understanding what constitutes normalcy within one’s own body empowers individuals towards making informed decisions regarding their health while recognizing when further evaluation might become necessary if unexpected shifts arise over time!