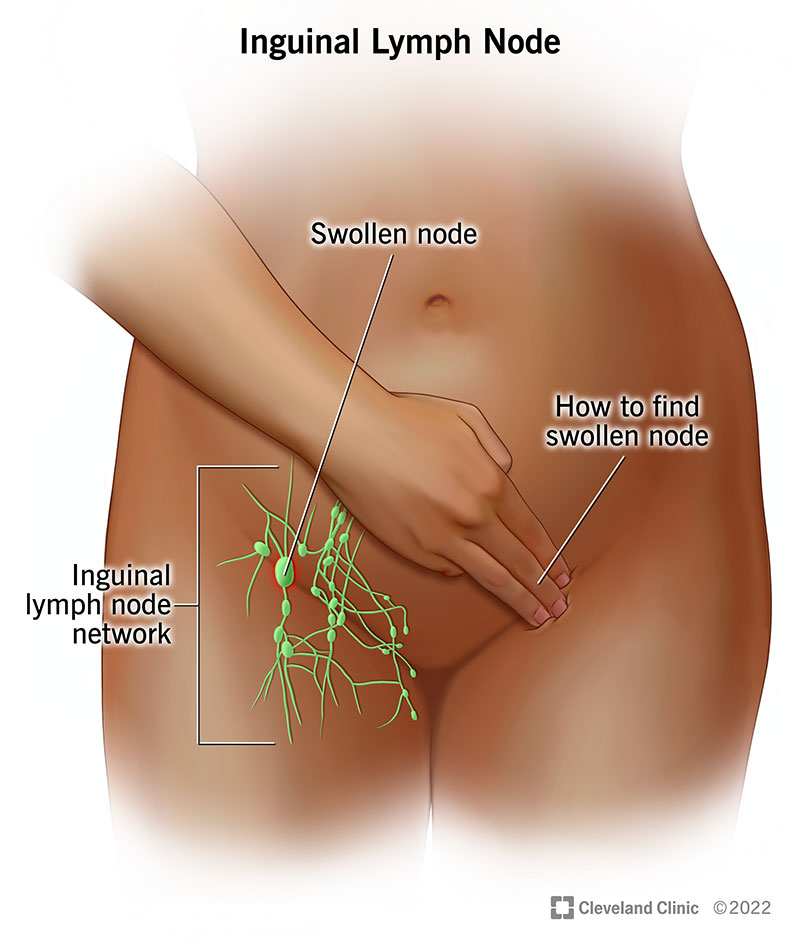
Cancer in the groin may indicate serious health issues, requiring immediate medical attention and thorough evaluation.
Cancer in the groin is a topic that often raises concerns, primarily due to its association with various types of malignancies. The groin area, which encompasses the junction between the abdomen and the thigh, is not just a simple anatomical region; it houses crucial lymph nodes, blood vessels, and nerves. When one talks about cancer in this area, it may refer to several cancers, including lymphomas, testicular cancer, and even metastatic cancers that have spread from other body parts. Understanding these conditions is vital for anyone who may be experiencing symptoms or has concerns about their health.
Understanding Groin Anatomy
The groin region is anatomically significant. It includes not only the superficial structures but also deeper components that play essential roles in bodily functions. The inguinal canal, a passage in the lower abdominal wall, allows structures like the spermatic cord in males and round ligament in females to traverse from the abdomen to the external genitalia. This area is also rich in lymphatic vessels and nodes that are critical for immune response.
The lymph nodes located in this region are particularly important because they filter lymph fluid and can be sites where cancer spreads or originates. A thorough understanding of groin anatomy helps demystify how cancer can affect this area and why symptoms should never be ignored.
Feel Better, Live Better — Every Day
Mind, body, soul — get inspired weekly with our expert wellness & nutrition tips.
Types of Cancers Associated with the Groin
Several types of cancers can manifest symptoms within the groin area. Here’s a closer look at some of these:
Testicular Cancer
Testicular cancer primarily affects younger men but can occur at any age. Symptoms often include lumps or swelling in one or both testicles, which may extend into the groin area. Early detection is crucial for effective treatment. Regular self-exams help identify any unusual changes early on.
Lymphoma
Lymphomas can present as swollen lymph nodes in the groin. This type of cancer affects the lymphatic system and can arise from various causes. Hodgkin lymphoma typically presents with painless swelling of lymph nodes, while non-Hodgkin lymphoma can have more varied symptoms.
Penile Cancer
Though less common, penile cancer can also lead to swelling or changes in the groin region. Symptoms may include growths or sores on the penis or scrotum that do not heal.
Metastatic Cancer
Cancers from other body parts can spread to the groin area through lymphatic channels or blood vessels. For example, prostate cancer frequently metastasizes to nearby lymph nodes, leading to swelling and discomfort.
Symptoms Indicating Possible Cancer
Identifying early signs of potential malignancies is vital for better outcomes. Common symptoms associated with cancer in the groin include:
- Swelling: Enlarged lymph nodes or testicles.
- Pain: Discomfort or persistent pain in the lower abdomen or groin.
- Changes: Unexplained changes in skin texture or color around genitalia.
- Lumps: Presence of unusual lumps that were not previously noted.
- Systemic Symptoms: Unexplained weight loss, fever, night sweats.
Each symptom deserves attention; ignoring them could delay diagnosis and treatment.
Diagnosis of Groin Cancers
The diagnostic process for cancers affecting the groin involves multiple steps:
1. Medical History Review: A detailed account of symptoms and family history helps guide further investigation.
2. Physical Examination: A doctor conducts a physical exam focusing on areas like lymph nodes and reproductive organs.
3. Imaging Studies: Techniques such as ultrasound, CT scans, or MRIs provide visual insights into abnormalities.
4. Biopsy: If a suspicious mass is found, a biopsy may be performed to determine whether it is malignant.
5. Blood Tests: Certain markers can indicate specific types of cancers.
Each step is crucial for an accurate diagnosis and subsequent treatment plan.
Treatment Options for Groin Cancers
The treatment approach will depend on various factors including cancer type, stage at diagnosis, and overall health status.
Surgery
Surgical intervention may involve removing tumors or affected lymph nodes from the groin area to prevent further spread of cancer.
Chemotherapy
This systemic treatment uses drugs to target rapidly dividing cells throughout the body. It’s often employed when there’s a risk of metastasis or when surgery alone isn’t sufficient.
Radiation Therapy
Radiation therapy targets specific areas where cancer cells are present and is often used post-surgery to eliminate residual cells.
Targeted Therapy
This newer approach focuses on specific molecular targets associated with certain cancers, minimizing damage to healthy cells while attacking malignant ones.
Each treatment comes with its own set of potential side effects that should be discussed thoroughly with healthcare providers.
The Role of Lifestyle Factors
While genetics play a significant role in developing certain cancers, lifestyle factors cannot be overlooked:
- Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables has been linked with lower cancer risks.
- Exercise: Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces risks associated with various cancers.
- Avoiding Tobacco: Smoking cessation significantly decreases risks associated with numerous malignancies.
- Regular Check-Ups: Routine screenings based on risk factors ensure early detection when treatment is most effective.
Making informed lifestyle choices contributes significantly to overall health and well-being while potentially lowering cancer risk.
Support Systems for Patients
Facing a cancer diagnosis can be overwhelming; therefore, having support systems in place becomes essential:
- Family Support: Open communication with family members provides emotional relief during tough times.
- Support Groups: Connecting with others who share similar experiences fosters understanding and encouragement.
- Counseling Services: Professional counseling offers coping strategies tailored to individual needs during treatment journeys.
Navigating through a diagnosis becomes easier when support systems are robust and readily available.
Key Takeaways: Cancer in the Groin
➤ Immediate Attention: Cancer in the groin requires prompt medical evaluation. ➤ Common Types: Includes testicular cancer, lymphoma, and metastatic cancers. ➤ Recognize Symptoms: Swelling, pain, and lumps are critical warning signs. ➤ Diagnostic Steps: Involves history review, imaging studies, and biopsies. ➤ Lifestyle ImpactLifestyle Impact
Frequently Asked Questions: Cancer in the Groin
What are the common symptoms of cancer in the groin?
Cancer in the groin can present with various symptoms that should not be ignored. Common signs include swelling, which may manifest as enlarged lymph nodes or testicles. Pain is also a frequent symptom, often described as discomfort in the lower abdomen or groin area.
Other symptoms include changes in skin texture or color around the genital region, and the presence of lumps that were previously unnoticed. Additionally, systemic symptoms like unexplained weight loss, fever, and night sweats may occur, indicating a more serious health issue.
How is cancer in the groin diagnosed?
The diagnosis of cancer in the groin involves several crucial steps. Initially, a medical history review is conducted to gather information about symptoms and family history. Following this, a thorough physical examination focuses on areas like lymph nodes and reproductive organs.
Imaging studies, such as ultrasounds or CT scans, provide visual insights into any abnormalities. If suspicious masses are found, a biopsy may be performed to determine if they are malignant. Lastly, blood tests can help identify specific cancer markers.
What types of cancers can affect the groin area?
A variety of cancers can manifest symptoms within the groin region. Notably, testicular cancer primarily affects younger men and may present as lumps or swelling in the testicles extending to the groin. Another significant type is lymphoma, which often causes swollen lymph nodes in this area.
Peniile cancer, though less common, can also lead to changes in the groin region. Additionally, many cancers from other body parts can metastasize to the groin area through lymphatic channels or blood vessels, such as prostate cancer affecting nearby lymph nodes.
What treatment options are available for cancer in the groin?
Treatment for cancer in the groin varies based on factors like type and stage of cancer. One common approach is surgery, which may involve removing tumors or affected lymph nodes to prevent further spread. Another option is chemotherapy, which uses drugs to target rapidly dividing cells throughout the body.
Radiation therapy targets specific areas where cancer cells are present and is frequently used after surgery to eliminate residual cells. Lastly, targeted therapy, a newer approach focusing on specific molecular targets associated with certain cancers, minimizes damage to healthy cells while attacking malignant ones.
How can lifestyle factors influence cancer risk in the groin?
Lifestyle choices significantly impact overall health and can influence cancer risk. A balanced diet rich in fruits and vegetables has been linked with lower risks for various cancers. Regular physical activity helps maintain a healthy weight and reduces risks associated with several malignancies.
Avoiding tobacco use is crucial; smoking cessation greatly decreases risks related to numerous types of cancers. Additionally, undergoing regular check-ups based on individual risk factors ensures early detection when treatment is most effective.
Conclusion – Cancer in the Groin
Cancer in the groin encompasses several serious conditions requiring immediate medical evaluation upon symptom presentation. Understanding its possible forms—testicular cancer, lymphoma, penile cancer—and recognizing symptoms such as swelling or pain can lead to earlier interventions that significantly improve outcomes. Regular check-ups combined with healthy lifestyle choices contribute positively towards reducing risks associated with these conditions. Awareness remains key; by staying informed about potential issues related to this sensitive area of health care, individuals empower themselves towards proactive management of their well-being.